Dockit • AI Demand Letter Drafting
Dockit is an internal application that supports case managers in handling claimant data, medical record requests, and case preparation for litigation. In the personal injury line of business, one of the most time-consuming tasks is drafting demand letters. These letters are critical: they compile liability findings, medical proof, and damages to request compensation from insurance companies.
Type
Case Study
Timeframe
1 Month
Toolkit
Figma, Figma Make, Loveable, V0, ChatGPT
Year
2025
Problem
Case managers are spending 4–6 hours per demand letter manually drafting in Microsoft Word. Even with ChatGPT for occasional assistance, the process is highly manual and repetitive, inconsistent in structure and tone, and a drain on time that could be spent managing more cases. Given the volume of letters and their importance in progressing claims, this bottleneck had a major business impact.
Solution
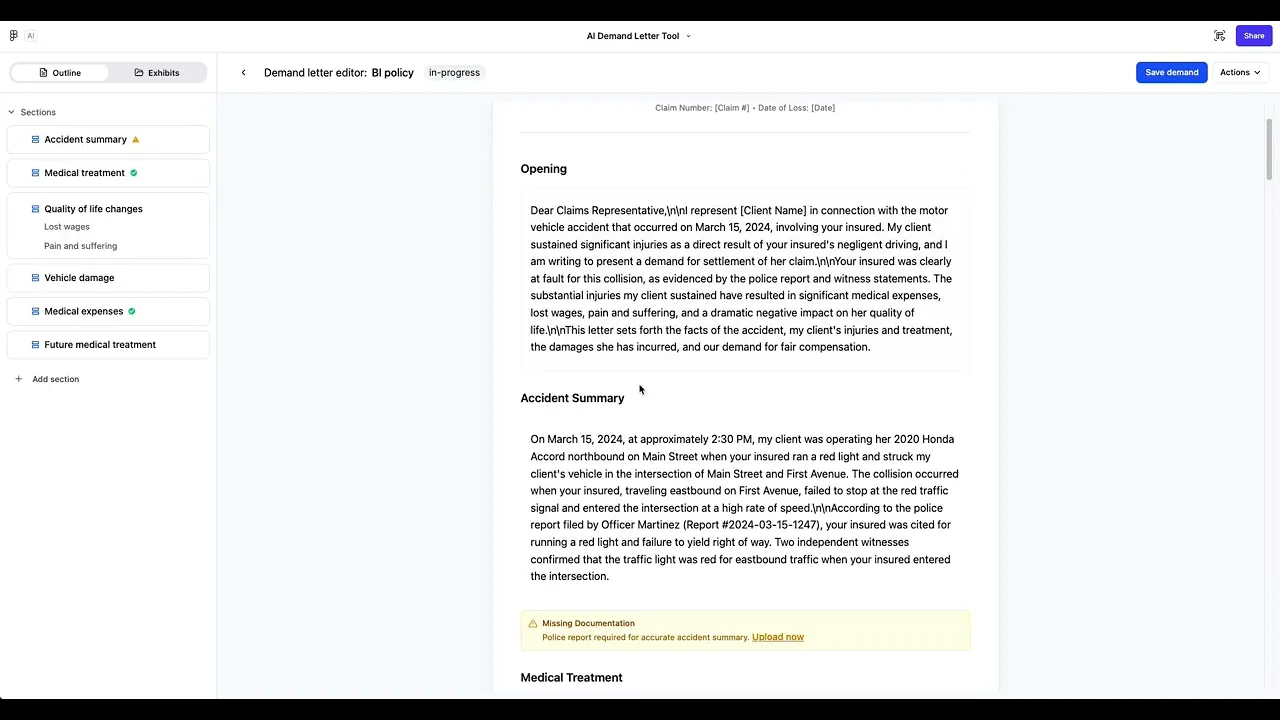
We built a Demand Letter Generator within Dockit that creates structured drafts directly in the settlement workflow. Case managers can select relevant sections and documents, organize exhibits with drag-and-drop, and edit drafts in a rich text editor with AI refinements. This shifted the process from manual writing to quick editing, cutting drafting time from 4–6 hours to about 1 hour while improving consistency across letters.
Research & Discovery
To ensure the tool matched real workflows, I partnered with five case managers and analyzed existing letters:
User interview takeaways:
The manual nature makes it hard for there to be consistency between the case managers, so the writing can vary depending on their writing style.
Most time was consumed by the Medical Treatment section, which requires precise injury documentation.
Letters are built section by section in a structured order.
Section content requirements vary by state law (at-fault vs. no-fault).
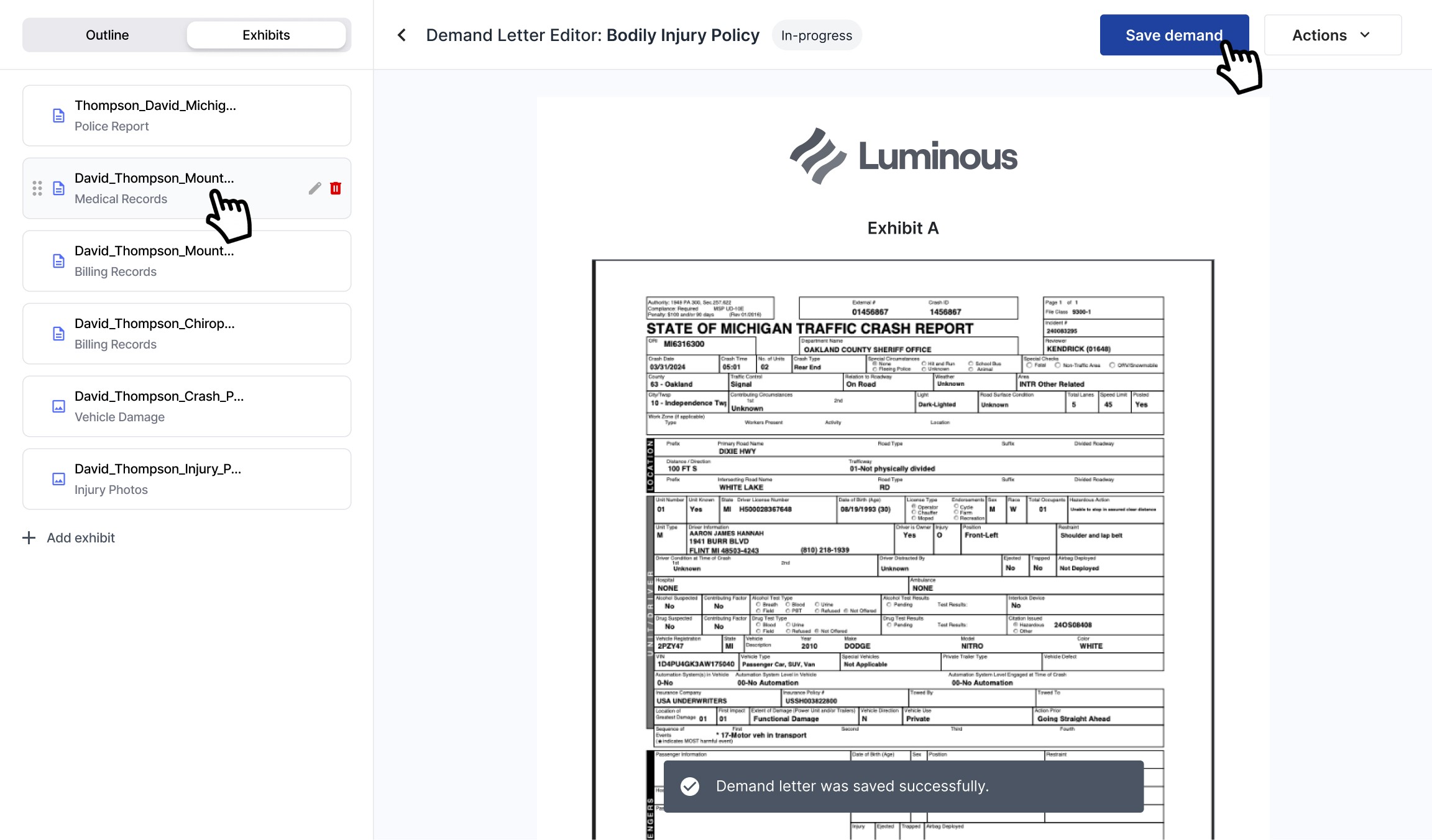
Exhibit management is just as important as the letter drafting.
Case managers emphasized exhibits (medical records, imaging, bills) as essential proof.
Managing these attachments within the same workflow was non-negotiable.
Production Demand Letter document analysis:
Reviewed 50 finalized demand letters.
Using ChatGPT, we broke them into discrete sections and identified what made each strong to gave a repeatable prompt library for consistent section generation.
These will be managed by LangFuse and can be edited as we go along.
Competitive Research
Identified top softwares used for AI demand letter generation.
Commonalities: Uploading all files needed to pull data from, initial data input for context, section by section text editing, exhibit management, and saving as you go.
The selling points to these softwares is their prompt generation models.
Constraints
Technical:
Document generation required background processing (chunkr) that could take up to 2 minutes.
Users needed the ability to leave and return while jobs processed asynchronously.
Design:
Letters had to be flexible for different state requirements.
The experience needed to feel natural within Dockit, not like a bolted-on feature.
Concept Ideation
Rapid Ideation Sketching

AI Prototyping
I created a Figma prototype to explore design directions and interaction patterns with the team. It wasn’t intended to be pixel-perfect, but rather a reference point to spark discussion and guide us toward the finalized design.
Design Solutions
Placement:
Integrated into the Settlements page, aligning with the start of the settlement process.

Workflow:
Create a new demand letter
Select sections & supporting documents
Generate draft in the background
Leave and return to edit, refine, and manage exhibits






UI patterns:
Left navigation: Section-based workflow for clarity and progress tracking
Main editor: Editable draft with formatting tools & inline AI refinement
Exhibit manager: Drag-and-drop interface for attaching proof to the correct sections









Outcomes
Time savings: Reduced drafting time from 4–6 hours to ~1 hour
Consistency: Predefined prompts & structured output improved letter quality and reduced variability
Scalability: Framework is adaptable to other case types beyond personal injury
User adoption: Case managers reported feeling more confident in consistency and relieved at the reduced manual writing load




